Chlorinated paraffins (CPs) are global environmental contaminants, but quantifying chlorinated paraffins (CPs) is challenging.

Prof. Chang'er Chen from SERI together with colleagues from Stockholm University, Sweden, developed a novel method for the quantitative determination of chlorinated paraffins (CPs) using bromide-anion attachment atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry (APCI-MS).This research was published in the lastest issue of Environmental Science & Technology Letter as front cover paper (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00216).
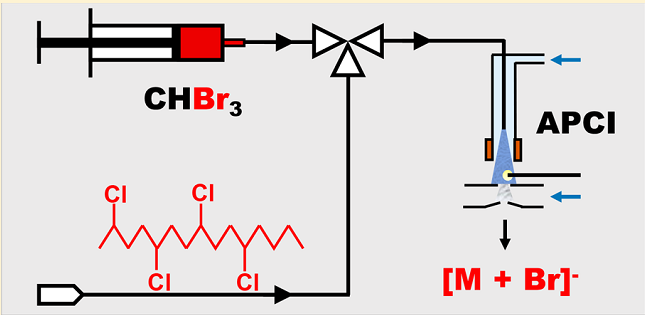
In this method, bromoform was used to enhance ionization of CPs. Near exclusive formation of stable bromide adduct ions ([M + Br]−) enabled accurate detection of individual CP congener groups (CnClm) with only a moderate-resolution quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Furthermore, the method was free from interference
commonly observed with chloride-anion attachment methods (e.g.,
decomposition ions [M + Cl – HCl]−) that require deconvolution. Together with a CnClm-response-factor algorithm for quantifying short-chain CPs and a CnClm-pattern-reconstruction
algorithm for quantifying medium- and long-chain CPs, method
applicability was demonstrated on biota and sediment samples. These data
were generated significantly faster and with improved selectivity and
sensitivity versus those of conventional measurements by chloride-anion
attachment APCI-MS.